An Outline to the Essay
This essay consists of an introduction, the theory, its impact, and a conclusion. The introduction talks about the journey of Charles Darwin that lasted for around two years in the ship HMS Beadle, the emergence of the Darwinism theory, along the individual that influenced the development of this theory. The main part of the essay is its body. This begins with the main factors that show the existence of evolution in this world. These factors indicated the presence of evolution and lead to the assumptions.
The next section is the theory itself, or the main postulates of the theory, which later called Survival of the fittest. The three basic things to understand regarding evolution namely, DNA, the quantity of DNA taking part in the change, and the effect of the environment on evolution, have been exhausted by this research paper. Next, the research paper has examined the seven stages of evolution recognized.
The study has examined solid evidence about the existence of evolution has also been examined, followed by arguments presented by different critics of Charles Darwin’s theory, and how they have been countered, until today. The paper then concludes by outlining an overview of the actual study.
Introduction
Not many books have caused as much uproar as the Origin of Species by Charles Darwin. This book was originally published in 1859 under the title, on the origin of species by means of natural selection or, The Preservation of favored races in the struggle for life (Darwin 2004, 56). The whole book and theory, if broken down into simplistic terms, just say that all living things developed from a single ancestor, and complex things developed from simple things. Over time, the genes of living things undergo genetic mutation, and the beneficial alterations were kept, which the author termed ‘natural selection’. These beneficial alterations were then passed on to the next generation and the process is continuing (Darwin’s theory of evolution 2009, par. 3). The theory had such a profound impact on the world of biology that the phrase “nothing makes sense in biology except in the light of Theory of Evolution” came into existence. Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection has engendered the “Darwinian Revolution”. Along with Darwin, his close associate, Alfred Wallace is also given credit for the theory. While traveling aboard the HMS Beagle for over two years, Wallace observed the fossils in South America, the Ostriches of the pampas, and the finches in the Galapagos Islands that triggered the research, leading to the proposition of the theory of Natural Selection.
The Theory and its Implications
Darwin and Wallace based their assumptions on seven basic factors that proved the existence of natural selection. These are Geology, Fossils, Island life, Overproduction of individuals, and extensive variation seen in individuals. These variations were inheritable and effects of artificial selection. It was found that geological procedures have been consistent throughout time, an indication of how considerably old the earth is. A glance at the present is enough to see the dynamics that shaped the past. Even slight changes that go on for a long period of time could have a large-scale impact, on Biology . Even though extinct, certain forms show a distant connection with the ones living, and this implied a thread of evolution running through both. While studying Galapagos Islands, it was found that the species within the islands were slightly different from their counterparts on the mainland. This led to the conclusion that the species that live on islands evolve in isolation, and thereby evolve slightly differently. According to Malthus, it was found that species reproduced exponentially. Even though offspring abounded, most of them did not reach maturity. This indicated a process of selection in which once members of an offspring reached maturity, reproduction would then occur. They also found that there were considerable variations within the individuals of a species. Both being taxonomists, they found that even the wild species were not an exemption. These differences were also innate. Even physiological traits, textures and body shape, vulnerability to certain types of diseases, etc., were also found to be inherited. While examining the methods of artificial breeding and their effect on domestic animals, it was found that some variations were favored and others were disfavored. Others were neutral even. These observed facts guided Darwin towards the theory of evolution and the principle of Natural Selection (Johnson 2008, par. 2). The Theory indicates that if a population of a particular species developed a functional advantage, like learning to fly, the progeny of that particular individual species would inherit this functional advantage, along with the successive generations. The inferior ones that remain behind would gradually die out. Natural selection means that the functional advantage of any particular species would be preserved and the remaining inferior members of the species would die out, leaving only the superior ones. This is very much like domestic breeding, where only the superior quality of a species is allowed to breed, leaving out the inferior ones. Natural selection singles out and discards the inferior members of a breed over time. The implication here then is that only those that are fittest would survive. Here, fitness means reproductive success [Darwin did not coin the term, Survival of the fittest’]. Darwin also wrote that these changes could not take place in giant leaps; rather, they would only occur progressively. Therefore, if any species contained a complex organ that could not have been formed by numerous, slow, and successive steps, this would have jeopardized the theory that Darwin so strongly supported. Such changes could also not take place in the individual members of a population but would happen to the whole population over periods of time.
Darwin states that the whole species must have developed from a common ancestor, which was the simplest organism, and from an event that took place by random chance. This, according to Darwin, is what resulted in the first form of life on earth. It is the development from simple to comple.
While one is examining the process of natural selection, there is a need to put into consideration three basic things:
- We need to know that only heritable variations are amplified or diminished. This is because of the controlling role of genes in these variations. Evolution happens because of the ability of genes to mutate. Genes are actually chemicals that contain coded information in the form of DNA. Though gene mutations are random, natural selection involving other factors happens.
- The whole population of a species gets involved in the process of Natural Selection as opposed to a single species.
- The process of natural selection depends on the environment. When the environment is friendly to a particular aspect of the species, members of a species that are not comfortable with the aspect in question end up reducing in numbers. If the environment alters, the species could return to its original habitat.
Under favorable environmental conditions, species variations due to natural selection could give rise to phenotypes.
One of the consequences of species variation due to natural selection is adaptation. Genetic reasons are believed to play a role in species variations and adaptations to the environment, as a result of Natural selection.
While considering the evolutionary chain, only the evolution between organic creatures is usually reflected. If we expand this universally and try to indicate the universal evolution cycle into this, we could divide the whole evolutionary chain into seven stages: Cosmic evolution, stellar evolution, chemical evolution, planetary evolution, organic evolution, macroevolution, and microevolution. Out of these seven stages, only the last evolution (microevolution) may be observed, according to scientists, while the rest are just assumptions.
Nevertheless, even though evolution is not observable directly, there is evidence that proves the theory to be true. First, we have to consider fossil evidence. While arranging fossils chronologically, we can notice a gradual change in the structure and formation of characteristic limbs of several species. For example, horses as a species show a very evident evolutionary trait. There is also proof to suggest that natural selection can evidently produce evolutionary change. It has been pointed out that birds like the finches [Darwin’s finches of the Galapagos Islands] are favored to have stouter beaks when only dry seeds are available to them.
Artificial studies indicate that evolution favors natural selection. Through research, we find evidence that points at the natural selection in other fields of Biology. A case in point here would be the anatomical record where organisms that share a common ancestry are found. The Molecular record indicates that the genes of organisms shown to be closely related by fossil records are also more similar than the ones distantly related.
Evidence also indicates that there are body parts that have been found to be remnants of our evolutionary past like the appendix and the tonsils, amongst others. These body parts have been found to have had no evident function at all within the body, but they still existed.
A century and a half after the publication of the controversial book by Darwin, this publication still holds its relevance in helping to better understand the field of evolution. The theory of evolution as championed by Darwin has raised many controversies. Darwin’s critics mainly raise the following objections to his theory.
- First the ‘theory’ is just a theory. There is no solid ground for the theory. We are not certain about the facts given in the books and in science, theory means the basis on which we can rely on. Critics argue that this argument has lost ground because even the theory of gravity is hypothetical too.
- Another thing pointed out at the time, was the absence of the fossil intermediaries. However, this argument has lost ground in recent times because the absent fossils have been dug up.
- There is the argument regarding what Darwin himself has said in his book, that it was difficult to imagine that the eye had developed with intermediaries, which he felt to be ‘irreducibly complex’. Even this argument has broken up because intermediate eyes have been dug up. These intermediaries arose upon the discovery of light, and it was better than not being able to identify it at all.
- The next argument is that the order of things is usually lost by the occurrence of random events as, stated in the second law of thermodynamics. However, the complete law stated is that of a closed system and the earth, which receives energy continually from the sun, and is therefore not a closed system at all.
- The formation of proteins by chance is a technical improbability, as Darwin’s opponents have stated. However, this argument was also proved wrong, in that the probability theory cannot be used to argue backwards.
- Another case is that Natural selection does not entail evolution. For example, there is nowhere that we find a fish developing wings and leaping away from predators in any of the experiments that have been conducted. Nonetheless, biologists argue that even in the case of lab experiments with dogs, breeds that cannot interbreed have been produced. This is also the case with evolution. Radically different species like fish and amphibians did have a common ancestor, a claim that is readily supported by available fossil records.
- The argument of such critics as the reducibly complex argument goes for the improbability of the complexity of a cell which cannot be explained by evolution from simpler stages. They seem not to understand that this happened eons ago and was set up stage by stage. The complex blood clotting system took nearly 600 million years to be fully formed. However, some varieties of fish retained the formative blood clotting system before its increase in complexity, to reach where it is today.
- Body parts, with no evident functionality, have recently been found to have had uses that were unknown in the past. This too, is an assertion made by critics of the theory of evolution, according to Darwin. However, such arguments are baseless, and the new-found functions of body parts like the appendix are neither an indication of the fallacy of the theory of evolution, or a proof of it.
Conclusion
Even though the concept of evolution was nothing new to the world of science, nonetheless many scientists preferred this to the concept of creation; they were not able to give an explanation to the process of evolution. Thankfully, Charles Darwin, using his theory of natural selection, greatly assisted in shedding light on the concept of evolution. The theory of natural selection that Darwin postulated has been a source of intense debate since the publishing of his book, ‘The origin of species’, in 1859. Notwithstanding the debates and controversies that have surrounded this theory, it has stood the test of time, for these 150 years.
Charles Darwin viewed evolution as a constant struggle to bring out the fitter species. That every species fights for life, is a fact accepted by everyone. Neo-Darwinism tries to reconcile the problem of accommodating Gregor Mendel’s theory, which states that species cannot be altered, with the theory of natural selection. Darwin has also argued that use and disuse mechanisms could be responsible for functional wing loss in selected insects dwelling in islands, indicating that natural selection could be at play here. Darwin was also convinced that environmental factors could be responsible for inheritable variations that were manifested by species. Even with the number of tens of thousands of ‘irreducibly complex’ systems at the cellular level, the cards pass on and on to both sides of the table.
Many are the times when people believe and accept that Darwin’s theory is the most acceptable for evolution. However, they do not go further to state that it does not prove evolution.
There have been many significant evolutionists in modern times who have revised the Darwinian theory of evolution. Under the light of modern inventions and developments in molecular science, the Darwinian science of evolution is now taking flight with new wings adapted for the horizon.
Reference
Bowler, Peter. J. 2003. The History of an Idea (3rd Ed.). California: University of California Press.
Campbell & Reese. Principles of Evolution. Web.
Darwin, C. The Origin of Species. London: Collectors library, 2004.
Darwin’s theory of evolution- A theory in crisis. 2009. Web.
Evidence for evolution- Controversial data. 2009. Web.
Evolution: Darwin’s theory. 2009. Web.
Johnson, George. 2008. The Evidence for Evolution. Web.
Johnson, George.2008. Backgrounders. Web.
Quammen, D. 2006. The reluctant Mr. Darwin. New York: Atlas Books.
Theory of Evolution. 2009. Web.
Thomas Huxley. 2009. Web.
Wallace & Darwin. Principles of Evolution. 2009. Web.
Appendix
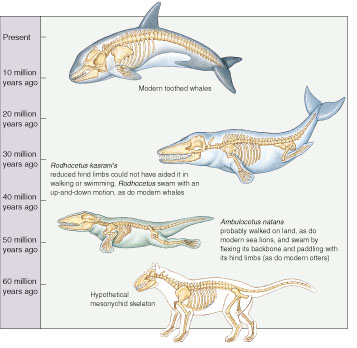
Proof of evolution of toothed whales from land-living hoofed animals.
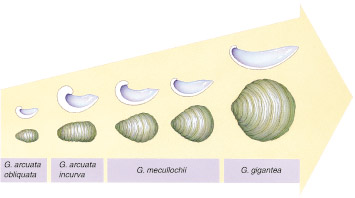
Evolution of flat small shelled oysters to large flat shelled ones in a period of 12 million years.
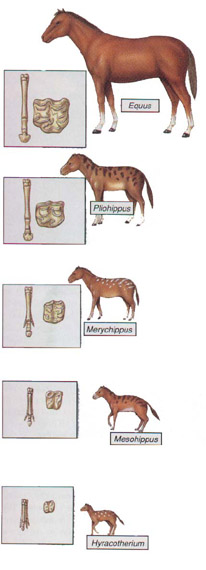
Fossil record of the evolution of horses from Hyracotherium to Equus. There are long periods of small change and small periods of great change.
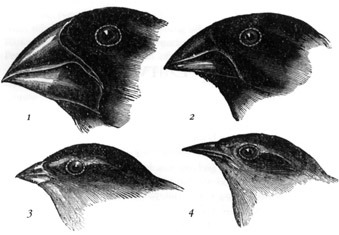
Darwin’s sketches of the Galapagos finches:
- Large ground finch Geospiza magnirostris;
- medium ground finch Geospiza fortis;
- small tree finchCamarhynchus parvulus;
- warbler finch Certhidea olivacea.
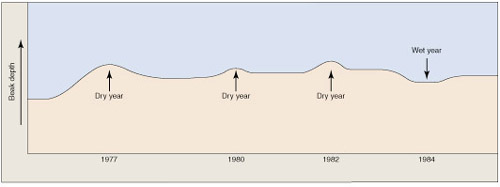
Evidence that natural selection alters beak size in Geospiza fortis.


These photographs show color variants of the peppered moth, Biston betularia. Tutt proposed that the dark moth is more visible to predators on unpolluted trees while the light moth is more visible to predators on bark blackened by industrial pollution
